An ongoing dialogue on HIV/AIDS, infectious diseases,
September 22nd, 2021
What I’ve Been Busy Doing, Besides Seeing Patients — and Bonus Animal-Related Infection Podcast

A 1914 postcard from New Zealand, where dogs have amazing abilities.
Long-time readers of this site (and I thank you deeply for that) might have noticed a lengthier gap than usual between today’s post and the previously published one.
Nearly three weeks! Wow! What on Earth is he doing? He must be really busy. That or just lazy.
In order to reassure you that the former is a better explanation for the silence than the latter, here are a few non-patient care things gobbling up the time that typically would go into crafting one of these posts:
1. ID fellowship interviews. COVID-19 notwithstanding, we continue to attract some truly brilliant, mission-driven, and just wonderful young physicians to this field. And can you blame them? It’s by far the most interesting and challenging medical subspecialty, arguably now more than ever.
But the process of reviewing applications, doing the interviews, and submitting our reports takes time — as it should. By the way, check out this paper that surveyed applicants and program directors after the first year of “virtual” recruitment to ID. Seems like virtual here to stay, at least in some capacity.
Just wondering — how many of those interviewees only put on the top half of their interview suits, and stuck with jeans, sweats, scrubs, or shorts for the bottom half? Zoom can’t tell!
2. The NEJM FAQs on COVID-19 vaccines. Or should I write Covid-19 vaccines? For reasons only the editors understand and are keeping secret from me, here on NEJM Journal Watch we write it as COVID-19, while in NEJM itself, it’s Covid-19. Go figure.
But if you know of another content area with greater changes day by day — sometimes hour by hour — than these amazing vaccines, it would be news to me. These FAQs require constant attention and updating, and even then one feels hopelessly behind. Talk about a Sisyphean task, one that might not get easier for some time.
Note that I am both very proud (and surprised) that I spelled “Sisyphean” correctly without looking it up and very grateful to Amy Herman at NEJM Group for her help on this giant project.
3. An opinion piece on the strange lack of guidance for booster doses with the one-shot J&J vaccine. Is the one-shot Johnson & Johnson vaccine less effective than the mRNA vaccines? Yes. Do we have evidence that giving an mRNA vaccine to prior adenovirus vaccine recipients boosts responses? Yes. Doesn’t even J&J think that its vaccine needs more than one dose?
Probably yes — their opinion further amplified by their press release of some of the ENSEMBLE2 data, though my co-author on the New York Times piece, Dr. Michael Lin from Stanford, still has some concerns:
https://twitter.com/michaelzlin/status/1440373910311034893?s=20
We’ll see. Regardless, it’s just so strange that with all the chatter about boosting the Pfizer-BioNTech (especially) and Moderna vaccines, the 14 million Americans who got one shot of J&J still wait for guidance. “Soon,” say many experts. Will be glad when that day comes.
4. Debating the top animal-related infections, with Dr. Jeanne Marrazzo. She’s the Chief of ID at the University of Alabama, a long-time friend and ID colleague, a scintillating conversationalist, and a true animal lover. One of my junior colleagues considers her a “hero” in ID. Who could be better for this O-F-I-D podcast? Note that I didn’t specify what I meant by “Top Animal Infection” — could be very serious, or having a cool life cycle, or just an amazing name, or having a great clinical anecdote, or some combination of all of the above.
So listen, learn, and laugh! And let me know in the comments if we left out one of your favorite animal-related infections. There are just so many.
(Quick aside — I got the idea for these silly drafts from one of my favorite writers in the world, Joe Posnanski. I even wrote him a fan letter! He does even sillier drafts with comedy writer Michael Schur on his “Poscast”, and gave me permission to do these Infectious Diseases ones since they don’t have overlapping content. He’s about to release a massive book, The Baseball 100. If you have even the slightest interest in baseball, I can’t recommend it strongly enough.)
(Transcript here, and also available on iTunes, Spotify, Overcast, or anywhere you get your podcasts.)
September 3rd, 2021
No, COVID-19 in Anti-Vaxxers Does Not Make Me Happy

Octopus Car Wash, Minneapolis, Minnesota; 1981. John Margolies’ Photographs of Roadside America (public domain).
High-profile people who deny the seriousness of COVID-19, or strongly oppose vaccination, also contract — and sometimes succumb — to the disease.
Surprise, surprise.
The list is long, but recently has included a group of well known conservative radio hosts. Broadcaster Marc Bernier from Daytona Beach, Florida, died of COVID-19 recently.
Bernier called himself “Mr. Anti-Vax”, so it follows logically that he was not shy about expressing his opinions. His last statement on social media compared government advice that people get vaccinated to Nazism.
He was dead less than a month later.
This week, Joe Rogan, a famous podcaster who explicitly discouraged vaccination among young healthy people, announced that he has the disease.
Unlike Bernier, Joe Rogan is recovering (at least as of his last communication). For treatment of COVID-19, he “threw the kitchen sink at it.”
While we might think that someone who refuses vaccination would take the same “natural” approach to therapy — allowing the body’s healing processes to save him without exogenous help — think again. He received monoclonal antibodies (a good move), ivermectin (shrugs), azithromycin (doesn’t work), prednisone (can make mild COVID-19 worse), an “NAD drip” (huh?) and a “vitamin drip” (available now pretty much everywhere).
Best V.I.P. treatment that money can buy! But for the record, our taxpayer dollars are paying for the one thing that probably helped, the monoclonals.
What I find fascinating about these cases of COVID-19 in disease-deniers and anti-vaxxers is our response — as a society in general and as ID doctors in particular.
If one reads the comments on line or on social media, here are some of the common attitudes:
- Anger. They got what they deserve.
- Glee. Schadenfreude in its purest form.
- What a waste. It’s unfair they take up limited resources for treatment.
- Natural selection. It’s Darwinian evolution playing out.
- A weary sadness. I just … can’t anymore.
It’s this last one — sadness — which overwhelmingly dominates ID doctors’ response. Some examples:
Deep sadness and ‘If only’– for them, their families and countless followers and their families …Sadness. Also validation. Followed by sadness about the validation … I will admit to feeling a sense of karma, but mostly it is just more and more sadness … Sad and powerless … Very depressed. It makes the weight of the last 18+ months heavier and heavier and it’s difficult to know how much more we can carry …When I think of their sphere of influence and their many unvaccinated followers’ deaths, which aren’t reported, it makes me incredibly sad …
At its most extreme, it’s a numb feeling, as highlighted here:
My emotional response is I can’t afford to have an emotional response. I just keep going. #IDTwitter. https://t.co/J9TSR3sf4T
— Jo Hofmann (@JoHofmann2) August 29, 2021
So don’t ask us if we’re glad to hear about another anti-vaxxer getting COVID. We’re not glad.
We’re very, very sad — and tired, too.
August 12th, 2021
Could This Be Our First Effective, Inexpensive, Widely Available Outpatient Treatment for COVID-19?

The Geometric Landscapes of Lorenz Stoer (1567)
It’s fluvoxamine.
This rarely used antidepressant, long off-patent, has quietly been going through high-quality clinical studies for treatment of COVID-19. It certainly won’t be endorsed or promoted by any deep-pocketed pharmaceutical company, but deserves some attention nonetheless.
Here’s why I think we might finally be onto something with this “repurposed” drug, even after stumbling numerous times with hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir-ritonavir, ivermectin, azithromycin, doxycycline, colchicine, et al.
First, there is a legitimate mechanism of action — actually, multiple mechanisms, as it has anti-inflammatory, anti-platelet, and potentially antiviral activity independent of its psychoactive properties. If you want to get into the weeds, read this nice summary. But of course many drugs have in vitro mechanisms of action that don’t pan out.
Next, Dr. Eric Lenze and colleagues published a small double-blind clinical trial — well-designed and conducted — which showed benefit. Out of 152 participants enrolled, clinical deterioration occurred in 0 patients treated with fluvoxamine vs. 6 (8.3%) patients treated with placebo, a difference that was statistically significant.
But the problem with such small studies is that a tiny shift in outcomes for the treatment group would substantially change the conclusion. In other words, the results were “fragile.” The authors appropriately concluded that further larger studies were necessary.
After this trial, there was an observational study of opt-in versus opt-out fluvoxamine among newly infected workers at a horse racing track. Despite having more symptoms at baseline, the opt-in group receiving fluvoxamine had better outcomes than those who declined treatment — specifically, 0/65 hospitalizations for fluvoxamine, vs. 6/48 who chose observation only.
But the observational nature of this study also couldn’t provide a high enough level of evidence to change practice. What if the people choosing fluvoxamine were just more “health seeking” — and hence healthier — than those who declined, biasing the result? A highly plausible explanation for the results.
Still, these studies got enough attention to warrant further research, and even a spot on 60 Minutes. The research includes the innovative TOGETHER trial, led by a multinational group of investigators primarily in Canada and Brazil.
Here’s the “adaptive” study design, which shows the tested candidate drugs and the novel way the investigators drop unsuccessful treatments:
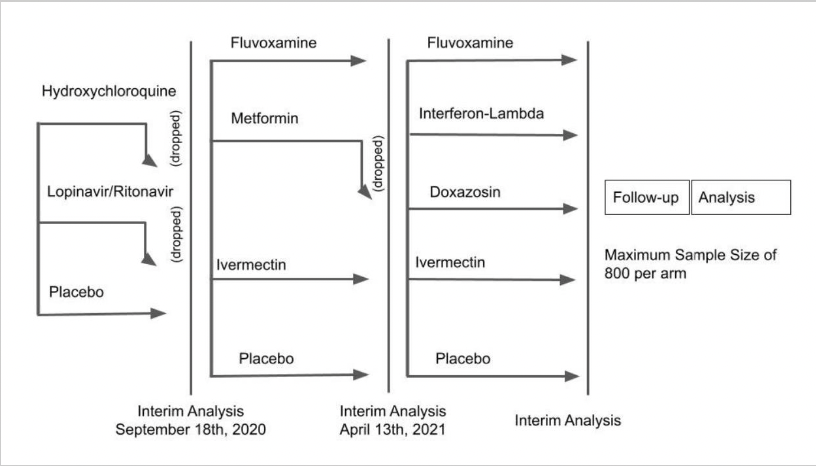
Eligible participants must have had symptom onset within the previous 7 days, a positive test for SARS-CoV-2, be older than 18, and have at least one risk factor for disease progression. The primary endpoint for these outpatient treatments was a composite of emergency room visits or hospitalizations due to the progression of COVID-19. The participants enrolled in 10 study sites in Brazil.
The group already published the negative results of their first study, showing that neither lopinavir-ritonavir nor hydroxychloroquine prevented progression to hospitalization or death better than placebo — which means those treatments have been appropriately dropped.
Time to move on to the next bracket, which included fluvoxamine, metformin, and ivermectin! Interim results were presented for the first time last week at an NIH meeting. The metformin didn’t do much of anything, and has been dropped; the ivermectin did a bit more, but still nothing practice-changing or statistically significant, with a relative risk of progression of 0.91 (95% confidence interval 0.69-1.19).
But the fluvoxamine treatment was much more promising. Among the 1480 participants randomized, fluvoxamine reduced the risk of disease progression by 29% (thanks to the lead investigator Dr. Edward Mills for this updated slide):
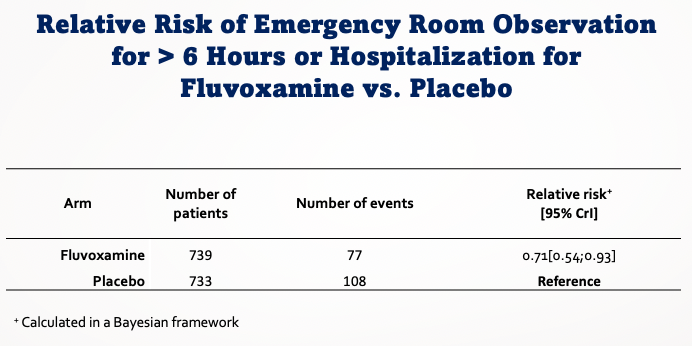
Most of the secondary endpoints also favored fluvoxamine, though the differences were not always statistically significant given the smaller event rate. No data on safety were presented, but Dr. Mills verbally stated that there were no unexpected toxicities.
No, an interim analysis of an ongoing study is not enough to change treatment guidelines — but it’s getting close, especially given the lack of other options and the favorable safety profile. The results are strong enough for the investigators to stop this comparison in this study, and no doubt a pre-print and submitted paper should be coming soon for further review.
Look, we’ve all been burned by promising studies of these repurposed drugs, and it’s quite reasonable to reserve final judgment until we see the complete data, and even other studies. Both the University of Minnesota COVID-OUT study and the NIH’s ACTIV-6 study include fluvoxamine arms.
But this already feels different from hydroxychloroquine and company given the high quality of the research. And it raises many interesting questions, including:
- Would the results be additive to monoclonal antibodies, which we know work well in early disease but remain limited in availability, expensive, and cumbersome to administer?
- How about combined with inhaled budesonide? Or with molnupiravir? (As an ID specialist with a research focus on HIV, you can tell I think combination therapy is a very good thing.)
- Should it be tried in inpatients, especially for those requiring oxygen, for whom anti-inflammatory approaches seem most beneficial?
- Would it work in other countries?
- On a global level, would fluoxetine be just as effective, as this SSRI is far more widely available?
- What should clinicians do now? Should they prescribe fluvoxamine for newly diagnosed patients with COVID-19? If so, for which ones?
No, I don’t have the answers. But this looks like progress, which during a pandemic is always great to see.
August 2nd, 2021
Provincetown July Celebration a Challenging Stress Test for the COVID-19 Vaccines
When the complete history of the COVID-19 pandemic is eventually written — and boy oh boy, can’t wait for that — certain events will feature prominently as sites of notable outbreaks.
The Diamond Princess cruise ship
The Biogen Leadership conference
The Skagit Valley Chorale practice
The Amy Coney Barrett White House reception
And now:
The Provincetown Independence Week celebration
So what sets the last one apart from the others? And why did it lead to a change in CDC guidance about masking indoors for vaccinated people?
The answer to question #1 is, of course, that the other events occurred before we had effective vaccines and the highly transmissible Delta variant.
But what about question #2? Why the reversal on masking indoors for people who have been vaccinated?
In addition to the sheer number of cases that occurred in vaccinated people, here’s the primary reason, in graphic form from MMWR: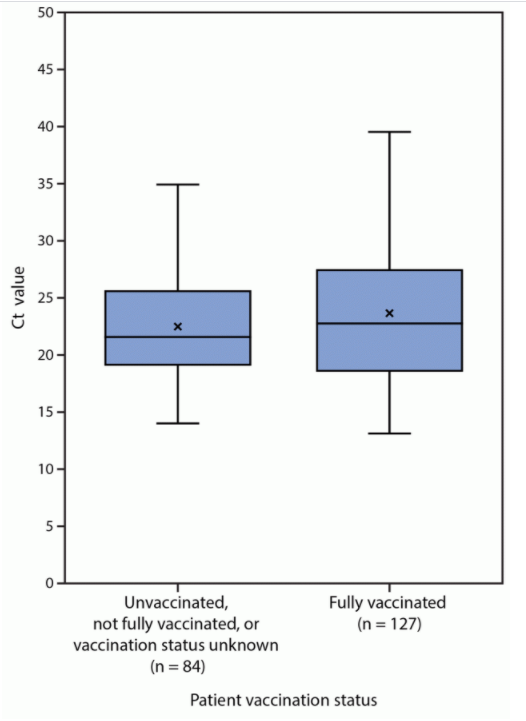
The vertical axis is the cycle threshold value, a measure of how much virus is in the sample (lower is more virus). And as is plainly evident, these results are similar for vaccinated and unvaccinated people.
These suggest that vaccinated people with COVID-19 could spread the virus to others as easily as unvaccinated people. It’s not proof, as it discounts the immune response, which may dampen contagious virus and shorten the duration of viral shedding.
It’s also in contrast with other studies that do show lower viral burdens over time in people who have been vaccinated — including this highly relevant recent study from Singapore:
A recent study out of Singapore shows not only does vaccination prevent you from getting sick with Delta (B.1.617.2), but it is associated with faster decline in viral RNA load. What does this mean? Vaccines make you LESS infectious!
— Chise (@sailorrooscout) July 31, 2021
Regardless, it underscores the plain fact that anyone with symptoms consistent with COVID-19 needs to isolate until recovery, vaccination status notwithstanding. For those diagnosed, we may even need to institute different isolation protocols, since the higher viral loads seen with Delta could mean more transmissions further out from onset of symptoms.
Already, the CDC has recommended that vaccinated people exposed to COVID-19 should get tested afterward, a return to pre-vaccine guidance. Should we also recommend antigen testing in breakthrough cases before return to work? (PCR may continue to detect non-viable viral fragments long beyond the contagious phase.)
What the outbreak can’t tell us is how bad this would have been without vaccines at all. Yes, there were lots of cases, but so far relatively few hospitalizations, and no deaths. Yikes, the mind boggles.
Because if anyone is under the impression that Provincetown is the kind of sleepy Cape Cod small town made famous through Edward Hopper’s dreamy artwork, think again — this July celebration is the diametric opposite. All who attended reported plenty of crowded bars, restaurants, and dance parties, with many shared accommodations among travelers.
You could hardly imagine a better environment for SARS-CoV-2 transmission. These settings plus the Delta variant provided the ultimate stress test for the vaccines.
What the outbreak also can’t tell us is how commonly asymptomatic people who are vaccinated acquire SARS-CoV-2 and then transmit it onward. This question has been filling up the email inboxes of every ID specialist out there.
I suspect it’s uncommon. But let’s not be overconfident about anything related to this tricky virus, which has bedeviled us with unpredictable twists and turns from the start. Humility!
This is quite the figure, from a @CDCgov presentation.
Further evidence of the critical role of humility when it comes to predicting what's next in this pandemic, a lesson we all need to learn again and again.
H/T @washingtonpost https://t.co/1LnqGojF3V pic.twitter.com/IlymSsJOOX
— Paul Sax (@PaulSaxMD) July 30, 2021
Yes, that’s a scary figure. What to do in the meantime as Delta is surging?
Get as many eligible people vaccinated as possible. Remember, the vaccines reduce transmission risk in two ways:
- Decreasing the probability of infection in the first place, either symptomatic or asymptomatic
- Decreasing the duration of infectiousness for those who do get infected
That first effect is ironclad — no virus, no transmission. The second one is a bonus. The evidence is strong that both of these are in play with COVID-19 vaccines, as summarized in this superb review.
So approve the vaccines already, FDA! This will allow broader implementation of vaccine mandates in schools and workplaces.
Plus, when possible, we should limit socializing indoors to gatherings with other vaccinated people. Since not everyone can be vaccinated — kids under 12, for example — if you’re planning a large indoor event, go ahead and ask people to get tested ahead of time. We might ask even if everyone is vaccinated, especially if the event has immunocompromised guests. Good tests are widely available over the counter that can give results back in 15 minutes. Let’s use them!
And whatever is causing COVID-19 case numbers to decline rapidly in the United Kingdom and India, here’s hoping it happens here as well.
July 13th, 2021
To First-Year ID Fellows, Incredible Gratitude and Respect — Especially for This Past Year
Two things happened earlier this month in most U.S. hospitals — the academic year started, and the number of people hospitalized with COVID-19 reached a low point not seen since the early phase of the pandemic.
(No, hospitalizations are not down everywhere. We ID docs are very much aware that COVID-19 isn’t over. But the national numbers are historically low — single digits in my hospital right now.)
The turn of the academic calendar means it’s a good time to express gratitude to the ID fellows who just finished their first year — especially this year, because unless you went through it yourself, I would argue that these past two years could not have been more difficult for these trainees. Historically so.
Let’s start with early 2020, the second half of senior medical residency for most ID fellows just completing their first year.
In normal, non-pandemic years, senior medical residency acts as a wonderful consolidation of all that’s learned in the preceding two years. With fewer clinical demands, senior residents can master the intricacies of inpatient medicine, teach on intern and medical student teams, handle their outpatient clinics, check out subspecialty electives, and participate in research projects. Senior residents also plan the next phase of their lives by either applying for fellowships or looking for a “real” job.
And yes, there’s a certain amount of gliding on cruise control. Plus all kinds of wonderful camaraderie, celebrations, and parties.
But 2020 offered nothing like this for senior medical residents. Here’s Dr. Eric Bressman’s account when he was Chief Medical Resident at Mt. Sinai Hospital, describing spring 2020 in New York:
Pretty soon we were just completely inundated, both at Sinai and Elmhurst, Elmhurst even more so. And while we were working a lot on the weekends, during the week it was all administrative in terms of completely remaking the structure of our floors, completely remaking the schedules of the residents to design a safer experience, both for the patients and for the residents. And we were pretty quickly working 24 hours [a day] to try and get that done, and I probably didn’t have a day off for two months.
Safe to say that there was no cruise control for these residents. Lots of unplanned inpatient coverage needed, especially in the ICUs. And the celebrations and parties? Prohibited for infection control reasons.
Plus remember this — for people who had applied to and then matched in ID, they chose ID before COVID-19 was even a thing. What had they signed up for?
Yes, when they arrived to start fellowship last July, case numbers were down in some regions. But the first year of ID fellowship already has enormous challenges for multiple reasons, even without a pandemic. It’s hard! Rewarding too, but no piece of cake. A brief summary, including several items highlighted in a previous post:

I didn’t previously mention the “weird demotion,” but it’s true. July rolls around, and BAM! First-year ID fellows become beginners again. An internship redux, only now their entire clinical service consists of patients that medical and surgical teams can’t handle on their own (orange and red boxes in figure above). Challenging!
Then, as 2020 progressed, into the tricky mix of first-year ID fellowship came COVID-19 again.
In Boston, it was like a ghoul from a horror movie prematurely left for dead, only now back and just as strong and as scary as ever. COVID-19 wards reopened. ICUs again had critically ill patients, some of them shockingly young. Consults and pages about testing, treatment, and infection control all took off, including at night — but this time the rest of the hospital activities continued at the same time, in parallel. There was plenty of non-COVID-19 ID work to be done. Yikes.
I distinctly remember walking into our fellow work room one dark afternoon in December, two fellows sitting there nervously at their computers. For a bit, no words — then one said to me, quietly:
We all have COVID fear …
A completely understandable reaction to a completely terrifying situation, one we all shared. Only I strongly suspect, for reasons cited above, that the level of post-traumatic stress disorder experienced by first-year ID fellows seeing COVID-19 cases go up again probably clocked in at the 99th percentile or higher.
It was the combination of recapitulating their difficult senior residencies, the legitimate concerns about being overworked, the need to be the expert on a disease with still so many unknowns — plus the very real fear of personally catching the infection.
Which is why, when the first supplies of the vaccines became available to healthcare workers, and queries went out to prioritize vaccine recipients, the answer for us in ID was a no brainer. First-year ID fellows! Of course!
So thank you, just-graduated first-year fellows. You did an amazing job under such difficult circumstances. Enjoy both the relative calm that second-year brings with it, and this helpful owl trying to interpret a CT scan:
Trying to read a CT when radiologist read is pending pic.twitter.com/O919wIg2hK
— Adi (@IDdocAdi) July 11, 2021
July 1st, 2021
Five Reasons Why ID Doctors Are the Paperwork Champs
As they often do, the inquisitive folks over at Medscape polled doctors around the country on various topics.
This one hit home:
We're #1! https://t.co/4peKM1frWx pic.twitter.com/wwCrcXBrVI
— Paul Sax (@PaulSaxMD) June 17, 2021
Say what you will about Medscape’s methodology, or representativeness, or need for statistical analysis.
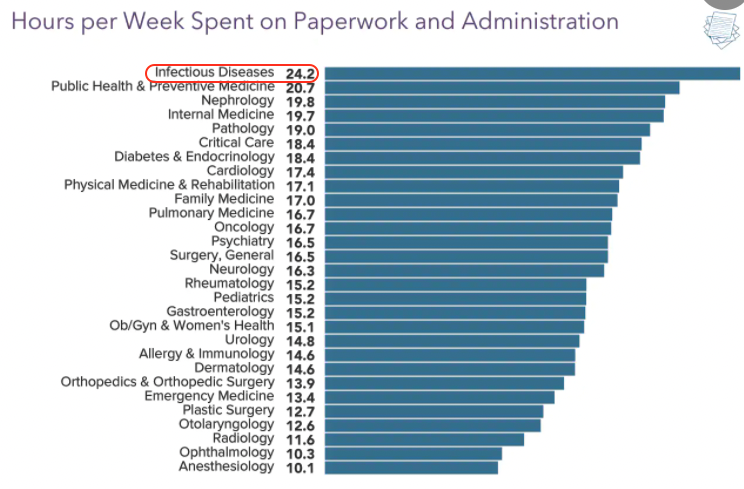
But we’re clearly #1 in the Paperwork and Administration category — and it’s not particularly close.
It’s also the very definition of a Pyrrhic victory — who wants this prize? — so let’s examine why this might be.
1. We take the best histories. We should celebrate this skill, as it is clearly our most important clinical procedure. After all, what other procedures do we generally do? That’s right, none.
But detailed histories take time — time to collect, and even more time to document.
Witness:
https://youtu.be/zHep6D_xxOo
These detailed histories, mind you, serve an important medical function and improve patient care — so often the critical missing piece of information arises in the process of collecting these data. I can much more strongly defend these histories than the common practice of cutting and pasting gobs of laboratory and other data into the note, the purpose of which is inversely proportional to its length.
Let the record show, however, that we were not put on this planet to provide the ideal source for a hospital discharge summary. Just imagine if we could collect royalties on every discharge summary that included a big chunk of an ID consult note — wow, we’d be golden.
2. We evaluate and manage complex patients — as a rule. Every doctor thinks their patients are the most complicated.
But since most straightforward ID problems are handled quite nicely by generalists, and no one gets an ID consult on patients who are doing well, the ID doctor’s rating of complexity is like the scale used on the WeRateDogs site:
This is Muffin. She hopes there’s still a spot on the Olympic team for her. Very confident this video is all they need to see. 14/10 pic.twitter.com/2uOyrUwJIx
— WeRateDogs (@dog_rates) June 29, 2021
That’s right — every case ranks at least an 11 on a 1-10 complexity score. Often higher. Like Muffin going for a swim up there. 14/10, go baby go.
In one of my favorite examples, I’ll cite again the landmark STOP-IT trial on the duration of antibiotic therapy for abdominal infections. Every ID specialist looked at the inclusion criteria — intraabdominal infection and adequate source control (emphasis mine) — and thought, “Who are these patients with adequate source control? Do they even exist?”
We have a resident rotating on our consult service right now who just did a consult on one such patient, and she couldn’t believe the complexity (certain details changed): The abdominal infection saga started in early-2020, and included a diverticular abscess, intestinal perforation, enterocutaneous fistulae, ventral hernia repairs, infected abdominal mesh, 8 separate admissions to three different hospitals, and innumerable polymicrobial cultures growing nearly every bacterial species in the MALDI-TOF database. Plus several different candida isolates.
“Adequate source control.” Ha ha ha.
3. We don’t give up. Shared, with permission, is this rant:
https://twitter.com/Boghuma/status/1407837071667040259?s=20
In the thread is further information that this application process started two months ago. Oh, and a later update — it’s still not resolved.
Who hasn’t faced the same thing when trying to get outpatient coverage for a novel antimicrobial? Omadacycline, anyone? Albendazole (the pricing of which is a true crime)? Tedizolid? Isavuconazole? I suspect we could fund an entire ID salary on the person-hours it has taken us to get our first few patients started on injectable cabotegravir-rilpivirine, which included a request for prescriber information that I didn’t even know existed.
And don’t get me started on clofazimine, which once upon a time was available by prescription, but now — just read about this painful process. Arghh.
COVID-19 brought with it an entire world of paperwork that previously didn’t exist, just like the virus SARS-CoV-2. Anyone who has tried getting monoclonal antibodies approved for inpatients with persistent COVID-19 probably thinks “EUA” stands for “Extra Unnecessary Activity.”
But we don’t give up. Because getting these obscure (and often frightfully expensive) drugs for people with difficult-to-treat infections is very much in our job description. So we do it.
4. We all have OCD — obsessive-compulsive disorder. I’ll never forget the sign-out I received from the graduating first-year fellow when starting my ID fellowship. A veritable tome, it weighed in at over a dozen single-spaced typed pages, each of them with the complete history, a detailed description of notable hospital events (surgeries, positive cultures, complications), antimicrobial courses (with doses), microbiology results, and assorted other factoids.
“I know it’s a lot,” she said, handing it to me. “But I’ve highlighted in yellow the things that need to be done today, and in blue those that might be important later.”
It was a color-coded masterpiece.
Look, we know we have a problem — and so does the rest of the medicine world, who gently tease us it about it periodically.
Here, take a look at the responses to this post:
What's more ID than writing an HPI that starts, "Briefly …"
… and then following it with a 1500 word note?
— Paul Sax (@PaulSaxMD) March 22, 2021
Many good responses, but this one truly captures it, from Dr. Joseph DeRose: “I do this as a prompt to tell myself to be concise … never works.”
Yep.
5. We don’t feel comfortable delegating work to others. I’ve thought about this one ever since my friend and neighbor, a thoracic surgeon, told me he had no trouble with our complex new electronic medical record.
“Barely look at it,” he said. “That’s what our PAs are for.”
Yes, he’s got a veritable army of support staff taking care of his patients — not just skilled PAs, but nurses, secretarial staff, scribes — and their responsibilities include note writing, prescription refills, prior approvals, insurance issues, filing, OR scheduling, patient transport, and likely also when to put new birdseed in his finch feeder.
No doubt this support he gets versus your typical ID doc is proportionate to the RVUs (otherwise known as RVU$) generated by an thoracotomy compared to a fever of unknown origin consultation. Still, the disparity remains quite stark.
But it’s not just that — often even when we ID doctors do have support staff to help us, we end up just doing things ourselves. I found one of my colleagues standing by the fax machine, in the process of sending a lengthy document to a skilled nursing facility so the staff there had the latest discharge summary on her patient. I asked her why she didn’t ask one of our (very nice) clinic staff to do it for her, and she looked at me as if I were some sort of prima donna physician, too elite to get his hands dirty using our ancient fax machine, which requires a hand-crank for power.
Yes, she’s as dedicated a doc as you could imagine — but is faxing documents a good example of a highly trained physician “practicing at the top of their license”?
So those are the Top 5 Reasons why ID is #1 when it comes to paperwork.
I’m sure there are others, but I don’t want to get all OCD about it!
June 14th, 2021
The Time for Hospitals to Require COVID-19 Vaccination Among Employees Is Now

Drs. Harry Meyer and Paul Parkman examine the rubella vaccine. National Library of Medicine.
Imagine you work at a hospital.
Patients come and go, admitted through the emergency room, or electively for surgery. Or they arrive for the day — maybe it’s an outpatient visit, or to receive chemotherapy or an infusion of biologic agents, or to undergo various imaging and other tests.
Some of them, of course, have weakened immune systems and won’t be fully protected by the COVID-19 vaccines. Others may not have received the vaccines based on poor access to healthcare or other social determinants.
Now imagine that you, healthcare worker, contracted COVID-19 because you’ve chosen not to be vaccinated. You feel well — in fact you are completely asymptomatic, blithely clicking the NO SYMPTOMS box in your hospital’s entry screen — but you’re in that brief period of being highly contagious.
And, as a result, you are the source of a COVID-19 transmission within the hospital to one or more of these vulnerable patients, and maybe some hospital coworkers (who could also be immunocompromised) as well.
How would that make you feel?
Importantly, the above chilling scenario is anything but hypothetical. An outbreak in a nursing home occured when one of the unvaccinated employees infected multiple residents and other staff. Even though 90% of the residents had been vaccinated, three of them died.
As cases continue to drop in the United States, we might need reminding that this is a highly contagious virus — even more so with the latest variants, which are 50% more transmissible than the original virus from China. Key graphic below, with estimated R0 for the increasingly dominant alpha and delta variants:
"The fact it has happened twice in 18 months, two lineages (Alpha and then Delta) each 50% more transmissible is a phenomenal amount of change"—@ArisKatzourakis https://t.co/A4M6dGfxSp
by @JamesTGallagher @bbchealth pic.twitter.com/PWvIiKYTVC— Eric Topol (@EricTopol) June 12, 2021
There is a solution, of course, one which would make the likelihood of in-hospital transmission to patients much less likely.
Hospitals can institute policies requiring that all employees be vaccinated.
Medical exemptions, of course, would be allowable. Some also would argue that documentation of prior infection would be sufficient — reinfection is rare. I’m fine with both, though do recommend vaccination for people with prior disease.
But what about the limbo “emergency use authorization” status of the vaccines? Shouldn’t we await full FDA approval? According to the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, employers may require vaccines for onsite workers as a means of protecting the safety of others despite this status.
This approach of mandatory immunization follows the model of required influenza vaccination (already widely in place nationally), but is arguably much more important — COVID-19 is more lethal than the flu, and the vaccines are more effective. Such a win-win-win for the individual, the hospital, and for public health overall.
As a result, it’s a policy we ID doctors — especially infection preventionists — strongly endorse. That’s why I was ecstatic when hearing that Houston Methodist, Penn Medicine, and Johns Hopkins, among others, all had put such rules in place. Our hospital is considering similar action.
Penn Medicine staff articulated their rationale in a NEJM Perspective, entitled Incentives for Immunity — Strategies for Increasing Covid-19 Vaccine Uptake. They cite a systematic review showing that requiring vaccination for employment is the most effective strategy to increase vaccination rates.
Vaccine requirements have enormous potential to improve public health. We know that school immunization policies here in the United States have kept our outbreaks of vaccine preventable illnesses among children much less common than in other countries, and we’ve actually eliminated one scourge entirely:
With vaccination requirements, more than 90 percent of children are protected against devastating diseases like polio and measles. Through vaccination requirements, smallpox was eradicated from planet Earth.
With the caveat that those interested in the musings of me, an ID doctor, are likely to think similarly, it appears that most agree that this is the way to go — if not now, then after full FDA approval:
Hopkins, Penn, Houston Methodist hospitals (among others) require Covid19 vaccination for employees since they may come into contact with patients. Is this the right policy? https://t.co/A7HbZ04lkC
— Paul Sax (@PaulSaxMD) June 12, 2021
But not all agree. More than 100 employees of Houston Methodist sued the hospital, saying that the mandate forced them “to participate in an experimental vaccine trial as a condition for continued employment.”
This is nonsense — getting the vaccine is not participation “in an experimental vaccine trial” — and fortunately a federal judge agrees, and dismissed the lawsuit. I’m hopeful that this action will pave the way for many other healthcare facilities to institute similar policies.
The bottom line is that it is a privilege to be in the position of taking care of patients, and with that privilege comes the responsibility of keeping them as safe as possible.
And that means getting vaccinated.
June 1st, 2021
We’re Allowed to Say that Some COVID-19 Vaccines Are Better than Others, Right?

Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Over on the CDC website, an amazing resource, there’s this statement about the COVID-19 vaccines:
The best COVID-19 vaccine is the first one that is available to you. Do not wait for a specific brand.
I certainly agreed with that comment back in late 2020 and early 2021, when demand for vaccines exceeded supply, and we faced record daily case numbers and a race against more transmissible variants, in particular B.1.1.7.
But fast-forward to today, and things COVID-19-wise in the United States have remarkably, wonderfully, changed. (Knocks wood.) Vaccine supply is plentiful. More than half the population has received at least one shot. Cases, hospitalizations, and deaths continue to decline.
Plus, we’ve got a much-expanded database on vaccine effectiveness and safety, in particular with the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer and Moderna, and an emerging sense of the J&J vaccine as well. Is the CDC’s statement still true?
Let’s take a look at the three vaccines available to us right now, comparing them in various metrics.
Effectiveness. We were appropriately cautious about making cross-study comparisons between results of the Pfizer and Moderna phase 3 studies versus those from the J&J study — different seasons, different variants, different geographic locations, different protocols.
But let’s be blunt — a difference between 95% and 60–70% efficacy in preventing symptomatic disease is pretty large. Plus, now we have many population-based studies of the mRNA vaccines showing 90% or higher effectiveness in clinical practice. Effectiveness studies for the J&J vaccine are just starting to appear, and the data look quite similar to the results from the clinical trial — in other words, around 70% effective.
Safety. Data on the rare — but serious — syndrome of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia (TTS) linked to the J&J vaccine were updated at the latest ACIP meeting on May 12. There have now been 28 cases after nearly 9 million shots. The median age was 40 (range 18–59), with 22 women and 6 men, with the highest risk among women ages 30–39 (roughly 1 case for every 80,000 doses). Again, amazing work by our vaccine safety program in identifying this important safety signal.
The mRNA vaccines, meanwhile, have no confirmed cases of TTS among over 245 million doses administered. Those are extremely reassuring data. Yes, subjective side effects are more common with the mRNA vaccines than with the J&J vaccine, and CDC now is tracking reports of myocarditis among younger people receiving these vaccines — connection still not confirmed — but many of these myocarditis cases have been mild. Meanwhile, some of the TTS cases have led to permanent disability and even death.
Boosters. It’s the question everyone wants to know — when will we need booster shots? From they are inevitable since antibody titers decline to never since cellular immunity is forever, the honest response is that we just don’t know.
But, if antibody titers are a marker for when we’ll need boosters, this modeling study shows a correlation between antibody titers and protection, implying we’ll need them sooner after the J&J vaccine than the mRNA vaccines. Which would not be very surprising with a one-shot approach, would it?
Convenience. Here the J&J vaccine should be the clear winner, requiring only one shot, and also being easy to ship and store. When we first heard of this advantage, many of us assumed this would mean a far greater supply and availability of the J&J vaccine. However, this is currently not the case, at least not yet. Manufacturing of the mRNA vaccines has clearly accelerated, and they are widely available in many diverse locations.
These differences are stark enough that I posted this poll last week:
Hey #IDtwitter — the @CDCgov writes, "The best COVID-19 vaccine is the first one that is available to you." Maybe true before, but now we're lucky, there's ample supply. So if you're advising someone, what would you recommend?https://t.co/toX4HW8zt9
— Paul Sax (@PaulSaxMD) May 24, 2021
It seems that most agree with me that the mRNA vaccines are now preferred. If you have a treatment or vaccine that’s both more effective and safer, you don’t need to be a disease modeler to figure out which one is better.
In the comments to this poll, some cited the contrast between where we are currently in the United States, and the situation globally — which remains dire, and still warrants a “first vaccine available” strategy. I cannot stress this point enough.
Others mentioned the importance of patient choice. I acknowledge this is an important consideration for individual cases — someone might need to reach that magic 2-week protected threshold sooner, or not have the time to come back for a second dose. These reasons could be enough to justify going forward with the J&J vaccine preferentially.
However, if someone asked me what COVID-19 vaccine I’d recommend, based on what we know now, my answer would not be “whichever one you prefer” or “whichever one you are offered first” — especially if it were a 35-year-old woman.
It would be an mRNA vaccine.
May 25th, 2021
Yes, the Yankees Had a COVID-19 Outbreak Even Though They’re Vaccinated — Here’s Why

John Clarkson, Boston Beaneaters, 1887. Library of Congress.
Hey Paul, aren’t you going to write something about the Yankees and their COVID-19 outbreak? How did this happen, aren’t they vaccinated?
So asked several of my friends, family members, and colleagues — understandably. I’ve never been shy about my unabashed obsession with baseball, nor my lifelong fandom of this particular much-reviled professional team, though it does earn me some good-natured ribbing here in Boston.
(I came to it honestly, having grown up in New York. And for the record, they were horrible the year I started rooting for them — 9th place. Yes I’m old, and yes that was quite the Impossible Dream year for the Red Sox.)
So here’s what happened with the COVID-19 outbreak among the Yankees, in as few words as possible: Nine people tested positive (mostly coaches and staff, one player). One symptomatic, with mild illness. All vaccinated, all with the J&J vaccine.
How could this occur? After all, with the vaccines so effective, to have nine breakthrough cases seems downright freaky, a bioterrorism plot hatched by Red Sox fans. Or if not that, an act of divine retribution for years of being America’s Most Hated Team.
With the caveat that I don’t have any inside baseball knowledge (you got that joke, right?), here’s how this could happen:
- The source of infection was a highly contagious person. The outbreak likely followed the over-dispersion model of SARS-CoV-2 spread, meaning one person spread to several others, rather than multiple different transmissions — a “super spreader” event, only with everyone vaccinated. This most likely happened indoors, and could have been introduced to the team originally from someone not vaccinated — but we don’t know that.
- A more transmissible or resistant variant likely caused the outbreak. Though the J&J vaccine did reasonably well in preventing infection in regions with circulating variants, there was some decline in efficacy in South Africa and South America. While I hope someone is sequencing these cases, sometimes the amount of virus in vaccinated people who test positive is so low (especially in those who are asymptomatic) that sequencing fails.
- The vaccine storage, cold-chain, and lot numbers need to be checked. Sometimes errors in vaccine handling happen that make it less effective. As if we needed a reminder that we’re still in unusual times, remember that baseball teams normally aren’t in the business of giving vaccines — they could have made a mistake.
- The vaccine isn’t 100% effective. This is the J&J vaccine, remember — 60-70% effective in preventing symptomatic disease. And even the mRNA vaccines aren’t 100% effective, as shown by this nursing home outbreak. But they sure do prevent serious outcomes!
- Most of these cases wouldn’t have been detected in the “real world” at all. Testing strategies in professional sports and the entertainment industry are intense, a far cry from what we do in the community. They test like crazy, especially once a case occurs, and generally have been using PCR — which picks up even fragments of viral RNA.
This last testing point deserves emphasis, because with all that swabbing and saliva collection — one report cited three times a day! — there’s a decent chance this kind of “outbreak” happens frequently all around us, but we just don’t know about it.
Regardless, the vaccine and the testing program did what it was supposed to do, meaning prevented severe disease, detected cases early, and prevented broad spread within the team. Most of the media coverage of the outbreak mentioned this favorable outcome.
Here’s a nice example, with an appropriate metaphor:
Cases that would have been hospitalizations become colds, and symptomatic cases become asymptomatic. Most infections are avoided entirely. The vaccine works like a strong head wind from the outfield, turning homers into doubles and doubles into harmless fly outs.
Love that!
And if the Yankees have any needs for an ID doc … my baseball achievements may have ended on my high school team, but I know an awful lot about antibiotics.
May 17th, 2021
CDC’s Surprise Mask Policy — and What It Means Right Now for Me

Edvard Munch, The Sun, 1911.
Anyone else out there blindsided by the CDC’s announcement last week about masks?
Fully vaccinated people can resume activities without wearing a mask or physically distancing …
Jeepers, that was fast. Less than a month ago, I was having a conversation with my dog Louie about outdoor mask mandates, wondering when our town would drop this unnecessary (in my opinion) rule about how we live out in the fresh air — where we know SARS-CoV-2 transmission is exceedingly rare.
But now, all at once, no masks needed at all for vaccinated people? Not quite — there’s plenty of fine print:
… except where required by federal, state, local, tribal, or territorial laws, rules, and regulations, including local business and workplace guidance.
That means we’ll still see masks in hospitals and doctors’ offices. Planes, trains, buses, airports. And this incredibly important caveat for our immunocompromised patients is a reminder that they can’t rely on the vaccines to protect them:
Well said, @CDCgov. The whole thing, but have highlighted something particularly important that often gets missed. https://t.co/aiUOs5nu4K pic.twitter.com/3KaJldDTmo
— Paul Sax (@PaulSaxMD) May 13, 2021
I’d add that many will continue to wear masks in settings like the crowded Trader Joe’s in my neighborhood, regardless of the policies they (or other companies) institute. Let me ask you — in places with sufficient density of people in public indoor settings, with the vaccinated status of many still not known, and case numbers still at tens of thousands a day nationally, why not wear a mask?
That’s what people like me will do. (Not that you need reminding, but I’m an ID doctor, living in a very mask-friendly state.)
In this piece, Zeynep Tufekci argued for CDC’s holding out a bit longer before making this policy statement — along with setting benchmarks for case numbers before removing indoor mask-wearing in public for vaccinated people. Several others have commented that they thought the announcement was premature.
I get that. But since half the country thinks this action by CDC is too soon, and the other half too late, the CDC’s probably getting it about right, timing-wise. Remember, local jurisdictions can make their own rules, people who have been vaccinated can make their own decisions, and there is a deep hope that this action will encourage those who have not yet been vaccinated to do so — it’s a tangible benefit.
So what happens next nationally? Strongly suspect we’ll see a continued downward count of case numbers, even with less mask-wearing. This is the combined power of the vaccines, which have proven to be remarkably effective in real-world settings, the shift toward outdoor activities, and exponential decay — fewer people out there with COVID-19 means fewer opportunities for new infections, an amazingly strong force we saw in play last summer even before we had vaccines.
Look, even with far more testing, we’re already back to where we were last June, and it’s only mid-May:
The last time the US had <17,500 confirmed cases in a day was June 8, ~11 months ago, when the testing was 1/3rd as much as now.
The descent (exponential decay) continues pic.twitter.com/ehb2LHP6qb— Eric Topol (@EricTopol) May 17, 2021
Believe me, I know that COVID-19 is not yet over — new cases still are occurring, and still will occur. Some will be serious, especially in the unvaccinated or the immunosuppressed. Some others will be in vaccinated people, mostly linked to indoor transmissions, as they always have been.
Remember, with this virus — humility. Stay flexible. Respond to new data. Keep on vaccinating.
And cheer these great numbers!


