August 11th, 2014
Study Offers Little Support for an Old Drug
Larry Husten, PHD
Digoxin is one of the oldest drugs in the cardiovascular arsenal, derived from the foxglove plant and first described in the 18th century by William Withering. It is frequently used in patients with heart failure (HF) and with atrial fibrillation (AF). The few trials supporting its use were performed in HF patients before newer treatments arrived. There have been no good trials in AF.
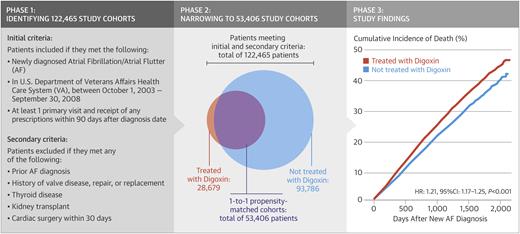
A new observational study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology now provides the most detailed perspective on digoxin use in AF. Researchers examined data on more than 122,000 patients in the Veterans Affairs system who had newly diagnosed AF. During 350,000 patient-years of follow-up, roughly one-quarter of the patients died. Nearly 29,000 patients who received digoxin were matched with an equal number of controls who did not. The risk for death was higher among digoxin recipients than controls — a finding that remained significant after multivariable adjustment:
- Unadjusted hazard ratio for digoxin patients: 1.37 (CI 1.33-1.40, p<0.001)
- Multivariate adjustment: 1.26 (CI 1.23-1.29, p<0.001)
The authors acknowledged the limitations of observational studies but said that their sensitivity analyses suggested that any effect of unmeasured confounders would not likely have resulted in a major change in the findings.
Responding to a question from the editors of CardioExchange, the lead author of the study, Mintu Turakhia, recommended that clinicians use digoxin sparingly: “in light of the many other drugs that can be used for rate control, clinicians need to ask whether digoxin should be the treatment of choice for the patient in front of them when there are other, safer alternatives.”
In an accompanying editorial, Matthew Reynolds praises the study but argues that since digoxin for AF is more likely to be used in higher risk HF patients the “true” hazard ratio is likely to be lower than reported. Given the high rate of adverse events caused by the drug, he recommends that digoxin should only be used “selectively and with care in AF patients.” But, he concludes, “for now, there are still clinical circumstances (HF, difficult rate control, low blood pressure) where this old herbal remedy remains useful.”
CardioExchange Editor Harlan Krumholz said that “this study raises concerns about the safety of digoxin in the treatment of patients with AF. Given the range of medications available, any use of digoxin in this setting should require specific justification indicating why the benefits outweigh the potential risks. It’s time to pause on digoxin until studies can assure that it is providing a net benefit to these patients.”
Note: Comments on this news story are closed, but please join the discussion about this topic over at Harlan Krumholz’s interview with Mintu Turakhia, lead author of the TREAT-AF study.